Introduction
Empathy refers to an aspect of personality, important in interpersonal relationships and in communication, considered to be an important value in the medical profession. In the present study, we have studied empathy in a sample of more than 5,000 medical students of all 43 medical schools in Spain.
Methods
The data belong to the DABE project, a study that included mental health variables and that was applied through a web survey just before COVID-19 pandemic restrictions started. To measure empathy, we used the Jefferson Empathy Scale (Student Version), which comprises 20 items relating to three underlying components, Perspective Taking, Compassionate Care, and Standing in the Patient’s Shoes.
Results
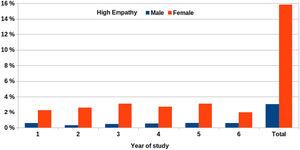
Empathy global score was high and it increased progressively every year during medical school. Empathy score was greater in the female students, with a 20% of participants showed high levels of empathy, again more in women. High empathy was associated with students having greater social support, more interest and participation in everyday experiences and satisfaction with social activities. The three components of empathy were also greater in women than in men. Empathy scores were significantly lower in those students that reported smoking and also in the students that reported use of frequent use of cannabis.
Discussion
Empathy scores are high in the spanish medical students population, with a 20% of them showing high levels. Empathy scores increase longitudinally during medical school, are greater in female students and lower in those smoking either tobacco or cannabis.

