Background
The objective of the study was to identify clinical and demographic factors predictive of hospitalization in primary healthcare patients diagnosed with suspected COVID-19 at the beginning of the pandemic.
Methods
A retrospective cohort study design was used. Patients attended in Casanova primary healthcare centre (CAP) (Barcelona, Spain) for symptoms compatible with possible or confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection between February 24 and May 30, 2020, were included. Data was collected through the electronic medical record and by telephone interview.
Results
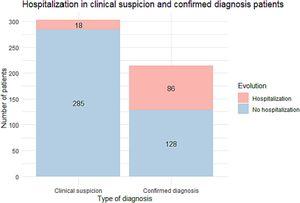
518 patients were included, of whom 283 (54.6%) were female. The median age was 50.2 years and 19.3% were aged ≥65 years: 79% were followed on an outpatient basis while the rest were hospitalized. Predictive factors for hospital admission were male sex, older age, a history of ischemic heart disease and the presence of dyspnoea, haemoptysis, nausea and vomiting, with a sensitivity of 48% and a specificity of 95.4%. Odynophagia and nasal congestion were predictors of a good prognosis. Mortality was 2.3% and 25% of deaths did not occur in hospital.
Conclusions
Nearly 80% of primary healthcare patients received only outpatient care. Male sex, older age, a history of ischemic heart disease and symptoms like dyspnoea, haemoptysis, nausea and vomiting could lead to a greater risk of an unfavorable evolution during COVID-19. Patients with at least one of the above factors, which correlate with a higher hospital admission rate, should receive a closer follow-up to early detect when they can benefit from a hospital evaluation based on their clinical evolution.