![[Translated article] Update on Lentigo Maligna: Diagnostic Signs and Treatment](https://multimedia.elsevier.es/PublicationsMultimediaV1/item/multimedia/thumbnail/S0001731023003198:gr1.jpeg?xkr=ue/ImdikoIMrsJoerZ+w9/t1/zx4Q/XH5Tma1a/6fSs=)
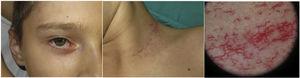
Lentigo maligna is an in situ cutaneous melanoma that arises in sun-damaged skin. Its most common presentation is a progressive, slow-growing, irregularly pigmented spot on the face of older patients. Although the exact percentage of lentigo maligna that progresses to invasive tumors is unknown, it is thought to lie between 2% and 5%. Both the clinical and histologic diagnosis of lentigo maligna can be challenging, especially in patients with early-stage or atypical disease. Treatment also holds challenges, because lesions are located in highly visible areas and are often large. Surgery can thus compromise cosmetic and sometimes functional outcomes. We review clinical and histopathological findings that can facilitate the diagnosis of lentigo maligna. We also examine treatment options, with a focus on surgery.