Introduction
Mir-146a-5p has been widely recognized as a critical regulatory element in the immune response. However, recent studies have shown that miR-146a-5p may also be involved in the development of Alzheimer disease (AD). Regrettably, the related mechanisms are poorly understood. Here, we investigated the effects of miR-146a in mice models and SH-SY5Y cells treated with amyloid β (Aβ)1–42.
Methods
To create a model of AD, SH-SY5Y cells were treated with Aβ1–42 and mice received intracerebroventricular injections of Aβ1–42. Then, the transcriptional levels of miR-146a were estimated by real-time PCR. We transiently transfected the miR-146a-5p mimic/inhibitor into cells and mice to study the role of miR-146a. The role of signaling pathways including p38 and reactive oxygen species (ROS) was studied by using specific inhibitors. Aβ and amyloid-beta precursor protein (APP)levels were measured by immunoblotting. Furthermore, Aβ expression was analyzed by immunofluorescence and histochemical examinations.
Results
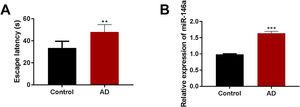
Aβ1–42-stimulated SH-SY5Y cells displayed increased transcriptional levels of miR-146a and APP. Moreover, the p38 MAPK signaling pathway and ROS production were activated upon stimulation with a miR-146a-5p mimic. However, treatment with a miR-146a-5p inhibitor decreased the levels of APP, ROS, and p-p38 MAPK. A similar phenomenon was also observed in the animals treated with Aβ1–42, in which miR-146a upregulation increased the expression of Aβ, p-p38, and ROS, while the inhibition of miR-146a had the opposite effect. This suggests that miR-146a increases Aβ deposition and ROS accumulation via the p-p38 signaling pathway.
Conclusions
Our research demonstrates that miR-146a-5pa increases Aβ deposition by triggering oxidative stress through activation of MAPK signaling.