Introduction
The growth hormone (GH) has been reported as a crucial neuronal survival factor in the hippocampus against insults of diverse nature. Status epilepticus (SE) is a prolonged seizure that produces extensive neuronal cell death. The goal of this study was to evaluate the effect of intracerebroventricular administration of GH on seizure severity and SE-induced hippocampal neurodegeneration.
Methodology
Adult male rats were implanted with a guide cannula in the left ventricle and different amounts of GH (70, 120 or 220ng/3μl) were microinjected for 5 days; artificial cerebrospinal fluid was used as the vehicle. Seizures were induced by the lithium–pilocarpine model (3mEq/kg LiCl and 30mg/kg pilocarpine hydrochloride) one day after the last GH administration. Neuronal injury was assessed by Fluoro-Jade B (F-JB) staining.
Results
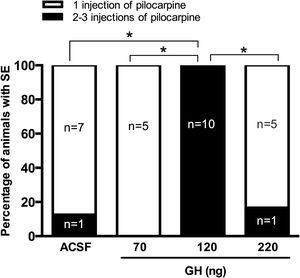
Rats injected with 120ng of GH did not had SE after 30mg/kg pilocarpine, they required a higher number of pilocarpine injections to develop SE than the rats pretreated with the vehicle, 70ng or 220ng GH. Prefrontal and parietal cortex EEG recordings confirmed that latency to generalized seizures and SE was also significantly higher in the 120ng group when compared with all the experimental groups. FJ-B positive cells were detected in the hippocampus after SE in all rats, and no significant differences in the number of F-JB cells in the CA1 area and the hilus was observed between experimental groups.
Conclusion
Our results indicate that, although GH has an anticonvulsive effect in the lithium–pilocarpine model of SE, it does not exert hippocampal neuroprotection after SE.
