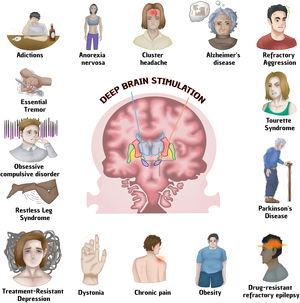
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) is a surgical procedure used to treat various neurological pathologies, being its greatest use in movement disorders. The FDA first approved deep brain stimulation in 1997 to treat essential tremor, in 2002 it was approved for Parkinson's disease, in 2003 for dystonia and in 2009 for obsessive compulsive disorder. However, until recently this technique began to be implemented for the treatment of other neurological diseases. To conduct research on the different neurological diseases where deep brain stimulation is used articles were chosen from Pubmed, Google Scholar, Redalyc and Scielo databases, references from the last 10 years to date were taken. The keywords that were written in the search engine were ECP/ECP + the required pathology. 75 references were found on the use of DBS in the following pathologies: Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's, refractory epilepsy, depression, obsessive–compulsive disorder, Gilles Tourette syndrome, aggressiveness, addictions, anorexia nervosa, restless legs syndrome, headache, dystonia, essential tremor and obesity. The use of DBS is growing as technology advances, increasingly focused on neurological diseases, psychosurgery and even systemic diseases, however, its use is only approved by the FDA for some movement disorders, including Parkinson's disease, Dystonia, essential tremor and OCD.