Introduction
Peer-assisted learning (PAL) has been extensively used in professional courses. However, its effectiveness as an adjunct to teacher-assisted learning (TAL) has not been evaluated. The objective of this study was to evaluate the effectiveness of Online PAL as an independent teaching methodology and as an adjunct to TAL, for dental students.
Methods
Forty BDS year 3 students were divided into 2 groups of 20 each. Four year 5 students were chosen as tutors to teach 4 different topics using the Microsoft teams platform. The study was conducted in two parts. At first, two topics were taught to one group by the tutor (peer-led group) and the other group, by a teacher (teacher-led group). Next, the remaining two topics were taught to both groups by the teacher initially. This was followed by repeated teaching of the topics to peer-led group by tutors, while other group did self-study. Students’ perception and performance scores were compared using an independent sample t-test for all the topics.
Results
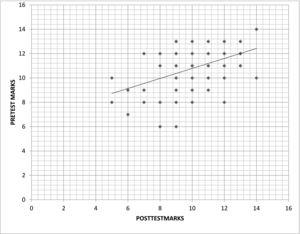
The mean performance scores in the teacher-led group for topics 1 and 2 were 86.15 and 90.22, whereas scores in the peer-led group were 75.38 and 79.21 which was statistically significant (p<0.05). The mean scores in the teacher-led group for topics 3 and 4 were 71.82 and 65.42, whereas in the peer-led group as an adjunct to TAL were 84.55 and 82.50. This was statistically significant (p<0.01).
Discussion
Online PAL as an adjunct to teacher-assisted learning can be useful for teaching dental undergraduate students.