Objective
To collect perspectives and explore consensus for expert recommendations related to asthma control and the use of telemedicine among professionals who manage patients with asthma.
Design
A Delphi-like questionnaire was designed to analyse the level of agreement about several recommendations formulated by an expert scientific committee about asthma control and the use of telemedicine with this purpose. A dedicated scientific committee validated the questionnaire, which included questions about the participants’ profile and the use of technological tools at a personal level or in clinical practice.
The experts expressed their agreement with a Likert-scale of 9 values: 1–3 was considered no agreement, 4–6 neutral, and 7–9 agreement. A rate ≥70% with the same answer was considered consensus.
Site
The questionnaire was programmed and distributed as an internet-based survey.
Participants
A pre-selected sample of 75 experts with experience in telemedicine (pulmonology, allergology, family medicine, nursing and community pharmacy) responded to a Delphi-like questionnaire composed by six questions and 52 items.
Interventions
Consultation was performed in two consecutive waves: the first wave was carried out from 12th of July to 8th of September of 2021; the second wave, from 25th of October to 12th of November of 2021.
Main measurements
Three questions about asthma control (actions for achieving or maintaining control of asthma at every visit, current problems that affect asthma control, and potential solutions to offset such problems), and three questions about the impact of telemedicine in asthma control (potential benefits of telemedicine, and potential reticence about telemedicine among both patients and healthcare professionals) were included.
Results
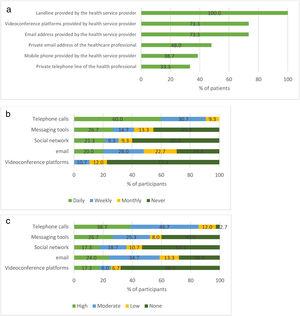
From the 52 items inquired, 35 were agreed by consensus. The actions for achieving or maintaining control of asthma, the problems that affect asthma control, and their potential solutions were agreed by consensus. The potential benefits of telemedicine were validated by consensus. None of the potential reservations of patients about telemedicine were validated, while five out of 14 potential reservations of healthcare professionals were agreed by consensus.
Conclusions
The COMETA consensus provides a current picture of the main problems for achieving asthma control, the benefits and the reservations about the use of telemedicine in the Spanish setting, and offers solutions. A wide interest in implementing telemedicine has been observed, although current limitations need to be overcome.