Introduction
To describe, validate, and evaluate the effectiveness of an in-house-developed mannequin versus standard commercial mannequins for emergency medicine training among undergraduate medical students.
Materials and methods
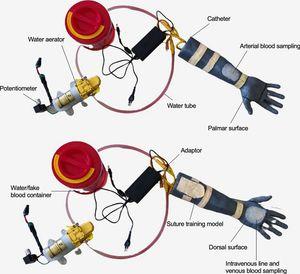
Firstly, we developed a 3-in-1 model consisting of 3 modules (sampling techniques, fluid resuscitation and IV drug administration, and minor surgery). Forty participants of 2nd-year medical students were enrolled. Each student completed three scenarios through the objective structured clinical examination (OSCE) simulation assessment. The questionnaire was used to rate the mannequins' overall quality, usability, comparability, cost efficiency, and realism.
Results
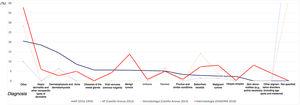
Although students using an in-house-developed mannequin had similar OSCE scores to a standard mannequin, students rated an in-house-developed mannequin easier to use. On the other hand, most students agreed that the standard commercial mannequin was more realistic than a substitute one. The costs of the materials needed for mannequin fabrication were less than 100 USD, and it was functionally comparable.
Conclusion
An in-house-developed mannequin was well accepted by students and teachers and could be used to deliver and assess clinical skills for medical students effectively at low-cost.