Objective
The aim of the study was to investigate the diagnostic value of an interferon gamma release assay (IGRA) – QuantiFERON-TB GOLD in-tube (QFT-GIT) – to identify new cases of active pulmonary tuberculosis (PTB) in Quzhou City, and to assess possible factors associated with false-negative IGRA results in bacteriologically confirmed PTB.
Methods
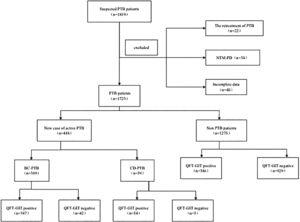
This study collected clinical data of suspected adult PTB patients who underwent QFT-GIT in Quzhou People's Hospital between January 1, 2020 and December 31, 2020, and calculated the total sensitivity, specificity of QFT-GIT in new case of active PTB patients were 90.9% (401/448) and 72.9%(929/1275), respectively. Univariate and multivariate logistic regression were used to analyze the influencing factors of the false-negative results of QFT-GIT.
Results
A total of 1723 patients were enrolled, including 448(448/1723,26.0%) with new case of active PTB (389 cases were bacteriologically confirmed and 59 cases were clinically diagnosed) and 1275 non-PTB patients. There were 747(747/1723,43.4%) patients with positive results of QFT-GIT, among whom 401 were new case of active PTB patients (347 cases were bacteriologically confirmed and 54 cases were clinically diagnosed) and 346 were non-PTB patients. The total sensitivity and specificity of QFT-GIT in the diagnosis of new case of active PTB patients were 90.9% and 72.8% respectively. In bacteriologically comfirmed PTB patients, multivariate conditional logistic regression analysis showed that BMI and diabetes, malignant tumors and severe infections were all independent risk factors for the false-negative results of QFT-GIT.
Conclusion
QFT-GIT showed high sensitivity and relatively low specificity in the diagnosis of new case of active PTB patients. In clinical practice, we should analyze the suspected PTB patients comprehensively in terms of whether they are overweight or complicated with diabetes, malignant tumors or severe infections, and avoid missing the diagnosis of PTB.