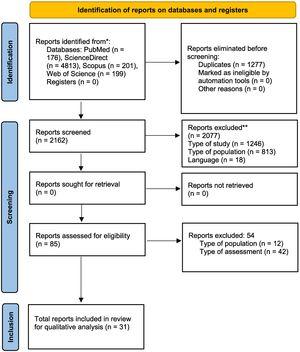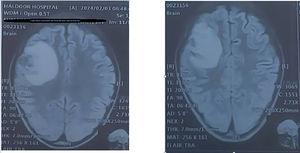
Tuberculosis (TB) is a chronic granulomatous disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, with extrapulmonary manifestations occurring in approximately 1% of cases. Among these, central nervous system involvement, including intracranial tuberculomas, is rare. We present the case of a 13-year-old female from Borama, Somalia, admitted with abnormal lip movements and a complex medical history, including weight loss, recurrent urinary tract infections, and a familial predisposition to TB. Neurological examination revealed left-sided facial deviation and hyperreflexia, prompting investigations that confirmed left temporal epilepsy and a right-sided tuberculoma. Treatment with levetiracetam and anti-TB medication led to significant improvement. This case underscores the importance of considering tuberculomas in the differential diagnosis of neurological presentations, even in non-HIV patients, especially in resource-limited settings like Africa.