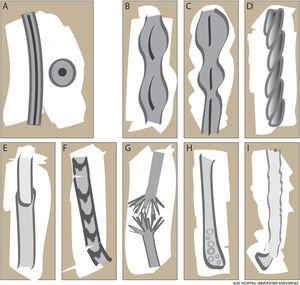
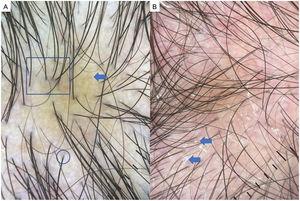
![[Translated article] Keys to the Diagnosis of Hair Shaft Disorders: Part II](https://multimedia.elsevier.es/PublicationsMultimediaV1/item/multimedia/thumbnail/S0001731022000540:gr1.jpeg?xkr=ue/ImdikoIMrsJoerZ+w9/t1/zx4Q/XH5Tma1a/6fSs=)
Hair shaft disorders, involving dysplastic abnormalities in the shaft, may be caused by genetic mutations or acquired through environmental exposures. The second part of this review presents these disorders classified according to the degree of hair fragility. It is important to take a thorough medical history and examine the hair to detect changes in texture, density, quality, and whether fragility is observed or not. Trichoscopy is a useful, noninvasive tool that can suggest a diagnosis in most cases. Specific treatments for hair shaft disorders are not available at present. We recommend general care practices to prevent hair damage; examples are avoiding excessive brushing, chemical products, hairstyles that introduce tension, and exposure to excessive heat. Some hair shaft disorders improve with puberty. Others may respond to treatments such as topical applications of minoxidil.