Artículos relacionados
Área salud
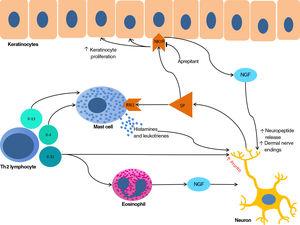
[Translated article] Update on Chronic Prurigo
diciembre 27, 2022
Área salud, Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas, Elsevier España, Medicina, Vol. 113. Núm. 6. (Junio 2022)
Chronic prurigo is itself a common condition, but it can also occur secondary to a large number of diseases. Management is challenging as historically chronic prurigo has been poorly defined and very few treatments are […]
Área salud
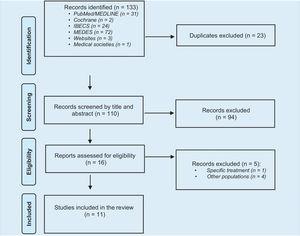
Humanistic and Economic Burden of Atopic Dermatitis in Pediatric Patients in Spain: A Systematic Review
mayo 16, 2025
Área salud, Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas, Elsevier España, Medicina, Vol. 116. Núm. 4. (abril 2025)
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a chronic, inflammatory skin disease affecting all age groups, particularly children. This systematic review provides an overview of the humanistic and economic disease burden in the pediatric population with AD in […]

Área salud
Clinical–Epidemiological Profile, and Treatment Response in Relation to Associated Atopic Comorbidity in Atopic Dermatitis. Experience From the BIOBADATOP Registry
mayo 16, 2025
Área salud, Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas, Elsevier España, Medicina, Vol. 116. Núm. 4. (abril 2025)
Background Despite advances made in treatments for atopic dermatitis (AD), information on its impact and interaction with atopic comorbidities, such as asthma, rhinoconjunctivitis, and ocular disease is limited. This study aims to assess the clinical–epidemiological […]
