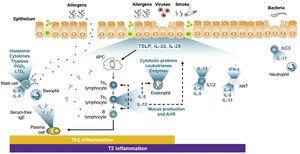
The excellent results for monoclonal antibodies in the treatment of severe uncontrolled asthma (SUCA) represent a milestone in current treatment of asthmatic disorders. Remaining, however, are several subsidiary areas for improvement in which new biologics are expected to make a decisive contribution. These biologics include tezepelumab, a monoclonal antibody that blocks thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP). TSLP is an epithelial-release cytokine (alarmin) that plays a key role in initiating both the innate (group 2 innate lymphoid cell (ILC) pathway) and the acquired (T helper 2 (Th2) pathway) immune responses by activating the type 2 (T2) asthma inflammatory pathway through both. It is also thought that it may additionally intervene in the neutrophilic non-T2 inflammatory pathway (via interaction with ILC3 and interleukin-17). Six clinical trials that included 2187 patients with uncontrolled asthma, with 2 or more exacerbations in the previous year, on medium/high-dose inhaled corticosteroids and at least 1 other controller, have demonstrated – irrespective of T2 endotype (and possibly also non-T2 endotype) – the efficacy and safety of tezepelumab, as it significantly reduces exacerbations (61.7%–66%) and bronchial hyperresponsiveness, and improves lung function, disease control, and quality of life. Tezepelumab could be indicated for the treatment of patients with, independently of the T2 phenotype (eosinophilic and non-eosinophilic), and may even be the only biologic available for treatment of non-T2 SUCA.